Chemistry
Synthesis
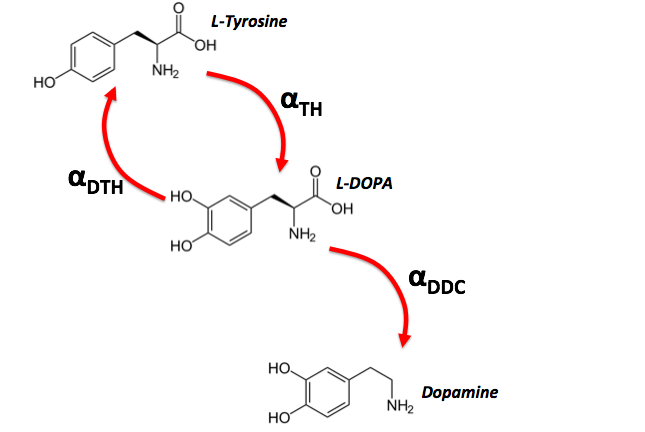
In the brain, certain neurons communicate with each other using the neurotransmitter dopamine. Dopamine is synthesized in a two step chemical reaction starting with the chemical L-Tyrosine. An enzyme TH converts L-Tyrosine into L-DOPA. L-DOPA is then in turn converted over into Dopamine using the enzyme DDC.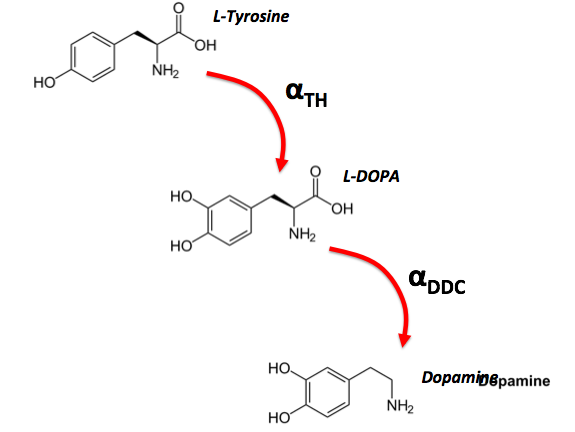
The rate constant of a reaction gives us the probability of a conversion in a given time step. Assume that L-Tyrosine converts to L-DOPA with rate constant \alpha_{TH}=0.4 and L-DOPA converts to Dopamine with rate constant \alpha_{DDC}=0.1. A molecule of L-Tyrosine is introduced to the system at n=0. This means that:
- \Pr(S_0 = \text{L-Tyrosine}) = 1.0
- \Pr(S_0 = \text{L-DOPA}) = 0.0
- \Pr(S_0 = \text{Dopamine}) = 0.0
Note: If a molecule doesn't change states on a time step it remains in the same state .
Answer the following questions; all answers should be accurate to within 10^{-3}. The solution boxes will accept python numerical expressions so feel free to enter your computations into them that way.
- What is the probability that the molecule is in the L-DOPA state at time-step $n=1$?
- What is the probability that the molecule is in the Dopamine state at time step $n=1$?
- What is the probability that the molecule is in the L-Tyrosine state at time step $n=3$?
- What is the probability that the molecule is in the Dopamine state at time step $n=3$?
Now assume you invent/discover a reverse enzyme dTH that modifies Dopamine production as shown (L-DOPA can now be converted back into L-Tyrosine).